Shedding Light on Cancer Diversity and Resistance
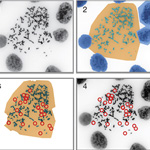
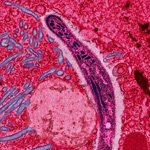
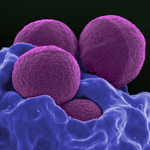
A paradigm-changing study in the journal Nature by cancer researchers and computer scientists at UC San Diego and other institutions found that short fragments of circular DNA that encode cancer genes are far more common in cancer cells than previously believed.