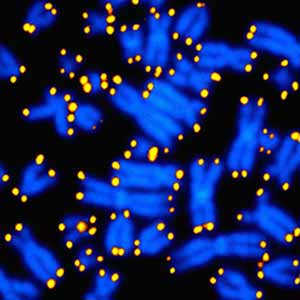
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Linked to Accelerated Aging
Writing in the May 7 online issue of American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Veterans Affairs San Diego Healthcare System suggest that people with PTSD may also be at risk for accelerated aging or premature senescence.