A New Strategy for Prevention of Liver Cancer Development
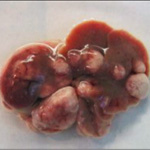
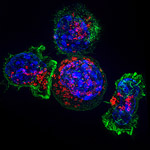
Primary liver cancer is now the second leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide, and its incidences and mortality are increasing rapidly in the United Stated. In late stages of the malignancy, there are no effective treatments or drugs. However, an unexpected finding made by a team of University of California San Diego School of Medicine researchers sheds light on the development of a new strategy for prevention of liver cancer.