Discovery Offers New Genetic Pathway for Injured Nerve Regeneration
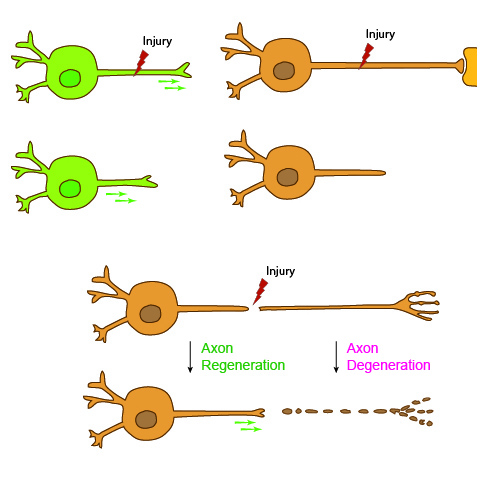
Researchers on the hunt for genes involved in regenerating critical nerve fibers came away with a surprise: The discovery of a new genetic pathway that carries hope for victims of traumatic injuries—from stroke to spinal cord damage. Although no cures exist for many nervous system injuries, if the damaged neurons do not die, “there is hope to find ways to make them stronger and help them regrow,” said senior author Yishi Jin.